
What is Indoor Navigation? The Complete Guide
What is indoor navigation? In this guide, you’ll learn:
- Why indoor navigation is a must for complex buildings and happier customers.
- How indoor navigation is used.
- And, how it works (plus, what technology works best for indoor navigation systems).
If you’re curious to understand how indoor navigation works, you’ll get a lot of value out of this guide.
Let’s dive right in.
What is indoor navigation?
Usually, a GPS is used to navigate from spot A to spot B. But as GPS doesn’t work well indoors, a different system is needed. That’s why indoor navigation or indoor wayfinding is used — and the industry is booming. In fact, Technavio predicts that the global indoor positioning and indoor navigation market will grow to USD 7.8 billion by 2021.
How indoor navigation is used
So, how is indoor navigation used? Simple: Users get a floor map that’s shown in an app or in a browser window on their smartphones or laptops. They can then search for locations and easily get guided to a specific spot with interactive step-by-step blue dot navigation.
(This video shows you how it works.)

What is Indoor Navigation
A user’s position is continuously updated. Accuracy ranges from about 1 meter to 5 meters. This depends on the technology used, building material, ceiling height, and so forth.
Indoor navigation technology is used in all types of complex buildings. These include: Airports, malls, hospitals, museums, offices, and stadiums.
Our own solution, NEARMOTION, has, among others, been used in health care facilities like Dallah Hospital and Johns Hopkins Aramco Healthcare (JHAH).
For example, indoor navigation can be used to find:
A particular store.
An elevator.
A hospital wing.
A gate at an airport.
The best route for people with disabilities.
Also, indoor navigation allows for people to receive push notifications and other content. In this way, you can send out timely information (such as timetables) and offers to visitors.
The benefits of indoor navigation
But what are the benefits of indoor navigation?
Good question. Indoor navigation will first and foremost improve the customer experience and increase visitor satisfaction.
You’ve probably experienced having to run from one floor to the next without finding what you’re looking for. That’s exactly the type of frustrating situation that indoor navigation helps to fix.
Indoor navigation is also used to lower costs, like staff costs. Plus, with the data you gather from your users, you can make smarter decisions about your space.
And finally, it can be used to engage visitors with relevant offers. For example, if someone walks towards a Starbucks, that person can receive a notification with a relevant offer.
How does indoor navigation work?
The technology that’s used for indoor navigation is an indoor positioning system (IPS) or indoor location tracking. The position is calculated on the user’s device, which is why this is called client-side positioning.
But what is the best indoor navigation system? Different technologies can be used for indoor navigation. These are:
Beacons
Indoor navigation used to be overly expensive. Today, effective indoor navigation technologies like beacons have lowered that price and in other ways made indoor navigation more user-friendly.

Beacon technology means that a space owner installs several small beacons in a building. These beacons transmit a continuous radio signal.
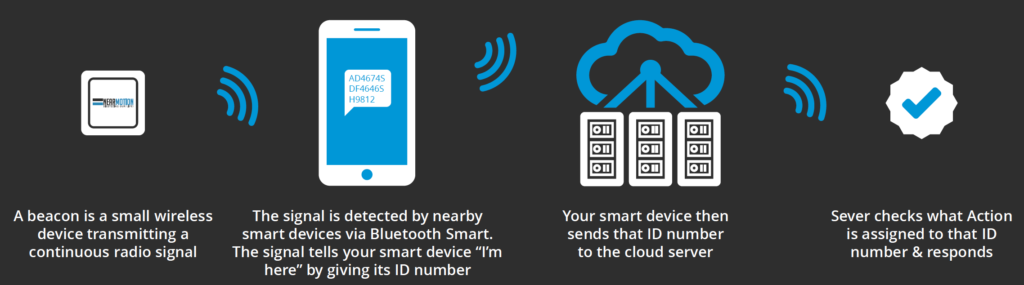
Nearby smartphones detect the signal via Bluetooth Smart. The signal gives an ID number that the phone then uses to identify a user’s location.
This happens in real-time. Instead of just showing a static map, beacons are used to guide people through a space.
For example, at NEARMOTION, we mainly use Bluetooth low energy beacons. Our positioning algorithm measures the strength of the Bluetooth signal that is transmitted from beacons. This signal is then detected by a smartphone.
The signal strength from different beacon devices is converted by the algorithm to a relative distances of which the exact location is detected.
WiFi-based systems
A WiFi-based system builds on tags that are WiFi transmitters. These tags send simple packets to WiFi access points in a building. The indoor navigation sensors calculate and report the time and strength of that reading. Algorithms can in this way find a user’s position.
The main problem with a WiFi-based indoor navigation system is that for an accurate solution, you need many access points. This makes the solution expensive and less power-efficient than other systems.
Ultra Wide-Band systems
Ultra Wide-Band or UWB transmits a wide pulse over a GHz of the spectrum and listens for chirps from ultra wide-band tags. The tags create a short and instantaneous burst so that ultra wide-band readers can report an accurate time measurement from the tags.
This system is relatively expensive because many tags are needed for accurate positioning.
Acoustic systems
Acoustic systems work like a UWB. The difference is that an acoustic system uses sound instead of radio signals. Receivers pick up the sound and locate tags. However, acoustic systems are still a niche technology.
Infrared systems
Infrared (IR) systems use infrared light pulses to locate signals inside a building. In every room, IR receivers are installed. The IR receiver then reads the device when the IR tag pulses.
The problem with an IR system is that IR readers need to be installed in the ceiling. If you have an open space, receivers will read the same pulse without identifying which reader is closest to the tag.
New technologies
Indoor navigation technology is constantly being developed and improved. For example, at NEARMOTION, we recently developed an Augmented Reality navigation solution.
And right now, we’re developing an indoor navigation solution based on Earth’s magnetic field that can be detected by built-in sensors in smartphones. This solution will further expand the use of indoor navigation systems to spaces where other solutions aren’t feasible. Additionally, it will offer an even simpler and more accurate indoor navigation system.
Want to learn more?
There you have it! If you’ve ever wondered “What is indoor navigation?”, you now know the answer.
To summarize, indoor navigation is a technology that will help ensure that your visitors and customers have a great experience. With it, you take out the frustration of navigating complex buildings, engage visitors, and increase your bottom line.
Want to learn more?
Get in touch today to see how we can help!
By: Camilla Hallstrom

Other news
Contact us
We are always open for new projects and ready to collaborate.



